Finding Area
Updated February 21, 2017 | Factmonster Staff 

See below for helpful information about finding the area of squares, rectangles, parallelograms, circles, ellipses, trapezoids, and triangles.
Square
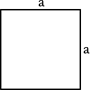 |
A = a2, in which a is one of the sides.
Rectangle
 |
A = ab, in which a is the base and b is the length.
Parallelogram
 |
A = bh, in which b is the base and h is the height.
Circle
 |
A = πr2, in which π is 3.1416 and r is the radius.
Ellipse
 |
A = πr1r2, in which π is 3.1416, r1 is the longer radius, and r2 is the shorter radius.
Trapezoid
 |
A = (h[b1 + b2])/2, in which h is the height, b1 is the longer parallel side, and b2 is the shorter parallel side.
Triangle
 |
Given base and height: A = (1/2)bh, in which b is the base and h is the height.
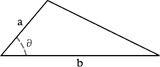 |
Given side, angle, side (SAS): (1/2) ab x sinθ, in which a is one side, b is another side, and θ is the known angle.
 |
Given three sides: ![square root of (s[s-a][s-b][s-c])](/images/math/almanac/A0876858-SQROOT-1.png) when s = (a + b + c)/2 (Heron's formula), in which a, b, and c represent the three sides.
when s = (a + b + c)/2 (Heron's formula), in which a, b, and c represent the three sides.
See also:
