Glossary of Chemical Terms - A
A
- achiral
- Describes any molecule or object that is superimposable upon its mirror image.
- acid
- A compound that produces hydrogen ions in water solution.
- acidification
- The process of increasing the hydrogen ion concentration.
- adsorption
- The concentration of a substance on the surface of another substance, which is usually solid.
- aerobic
- Living or active only in the presence of oxygen.
- aerogel
- A porous solid formed by replacing the liquid in a gel with a gas; what remains when the liquid part of an alcogel is removed without damaging the solid part.
- alcogel
- A gel formed by the coagulation of a sol in which the liquid is alcohol; at the gel point, the mixture forms a rigid substance that can stand on its own. The liquid and solid parts of an alcogel occupy the same volume.
- alcohol
- A class of organic compounds which has an OH group covalently bonded to a carbon atom.
- alkaline
- Describes an alkali (basic) or a solution that has excess of hydroxide ions.
- alkane
- A saturated hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n+2.
- alkylated
- A molecule that has attached to it an alkyl group (derived from an alkane - CnH2n+2), which is a saturated hydrocarbon with a single bond available.
- allotrope (allotropic form)
- Different bonding arrangements allowing for different forms of matter to be made from a single type of atom. Different forms of matter made in this way are called allotropes. For example, ozone (O3) and dioxygen (O2) are allotropes of the element oxygen. Also, diamond, buckyball, and graphite are allotropes of carbon.
- amalgam
- An alloy of mercury with another metal, often used as a dental filling.
- amide
- an organic functional group that has the following structure:
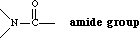
- amphetamines
- Any of the compounds which are substituted or slightly modified amphetamine molecules.
- amphoteric
- A compound that can act as a base and an acid.
- anabolism
- Metabolic synthesis of proteins, fats and other constituents of living organisms from molecules or simple precursors, which usually requires an input of energy.
- anesthetic
- A substance that produces loss of sensation, sometimes with loss of consciousness as well.
- angstrom
- A unit of length equal to 1 x 10-8 cm or .1 nanometer. It was named after A. J. Angstrom (1814-1874), a Swedish spectroscopist.
- anion
- A negative ion.
- anode
- A positive electrode; the electrode toward which electrons flow; the electrode at which oxidation occurs.
- anthropogenic
- Resulting from the actions and influence of human beings.
- antiaromaticity
- The unusual instability that results from a continuous cyclic system of 4n pi electrons (where n is any integer).
- antimatter
- Any subatomic particle identical in mass to a proton, neutron, or electron, but with the opposite charge.For example, a positron is a positive electron.A collision between a particle and its respective antiparticle results in both being annihilated, with their masses converted to photons of equivalent energy.
- antisense
- Having a sequence complementary to a segment of genetic material and serving to inhibit gene function.
- aquifer
- Water bearer. Earth materials that contain ground water and through which ground water may flow freely. Some examples of these include sand, porous sandstone, and gravel. Aquifers vary widely in their ability to hold water and the speed at which water flows through them.
- aromaticity
- The unusual stability that results from a continuous cyclic system of 4n + 2 (where n is any integer) pi-electrons in a cyclic compound. This stability results from complete filling of bonding pi molecular orbitals.
- asteroid
- Any of the thousands of small bodies that revolve about the sun in orbits lying mostly between those of Mars and Jupiter. Also known as a minor planet.
- atherosclerosis
- A disease of the arterial walls characterized by fatty deposits and abnormal tissue growth.
- atmosphere
- Unit of pressure equal to 101325 pascals or 760mmHg. Its symbol is atm.
- atom
- The smallest unit of an element which has all the properties of the element. It is composed of protons, neutrons and electrons.
- autoclave
- An airtight chamber use for processes requiring dry temperatures above 212 degrees F.
- Avogadro's number
- The number of particles present in 1 mole of a substance, experimentally determined to be 6.02 x 1023.
Glossary created by David Shaw (Madison Area Technical College) for The Chemistry Place.
Information Please® Chemistry Place, ©2005 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
| Contents |







