Chemistry: What Are Gases?
What Are Gases?
Gases are the phase of matter in which particles are usually very far apart from one another, move very quickly, and aren't particularly attracted to one another. Because the molecules in a gas are so far apart from one another, gases are much less dense than liquids or solids. For example, it's easier to pick up a huge balloon full of air than a huge water balloon.
We can see the differences between the structures of solids, liquids, and gases by looking at the following figure:
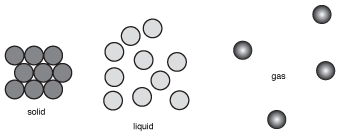
Figure 15.1(a) Solids consist of particlesthat are bound in place by a variety of relatively strong forces. (b) In liquids, the particles can move freely past one another because they are only held together by weak intermolecular forces. (c) The particles in a gas have almost no attractive forces at all, which allows them to spread out.
The reason that gases ignore any intermolecular forces (Solids) that might normally exist between the atoms or molecules is that they have enough energy to overcome the strength of these forces. For example, elements that experience weak intermolecular forces vaporize at extremely low temperatures (in the case of helium, -269º C). On the other hand, if a chemical compound is held together by strong intermolecular forces such as the hydrogen bonds in water, a much larger amount of energy is required to overcome these forces (H2O boils at 100º C).
The following are general properties of gases:
- Gases don't have a fixed shape. Gases fill the nooks and crannies of whatever container you put them in.
- Gases don't have a fixed volume. Unlike liquids, gases expand across an area until something physically stops them. This phenomenon explains why little old ladies who wear too much perfume can frequently be smelled long before you see them coming.
- Gases mix freely with other gases. Unlike liquids, which sometimes don't mix at all (e.g., oil and water), any combination of gases will always mix with one another.
- Gases can be easily compressed. Because there's a lot of space between the molecules in a gas, you can easily squish them down. Solids and liquids, on the other hand, are much less compressible.

Excerpted from The Complete Idiot's Guide to Chemistry © 2003 by Ian Guch. All rights reserved including the right of reproduction in whole or in part in any form. Used by arrangement with Alpha Books, a member of Penguin Group (USA) Inc.
To order this book direct from the publisher, visit the Penguin USA website or call 1-800-253-6476. You can also purchase this book at Amazon.com and Barnes & Noble.
