DK Science & Technology: Circuits
An electric current flows in a loop, powering bulbs or other electric COMPONENTS. The loop is an electric circuit. A circuit is made up of various components linked together by wires. The current is driven around the circuit by a power source, such as a BATTERY.
Table 26. CIRCUIT DEFINITIONS
| Voltage | is the energy given to each unit of charge that flows in a circuit |
| Current | is the amount of electric charge flowing past a point in a circuit each second |
| Wattage | is the amount of electrical energy a circuit uses each second |
Electric current is a flow of electric charge (usually in the form of electrons) through a substance. The substance or conductor that an electric current flows through is often metal wire, although current can also flow through some gases, liquids, and other materials.
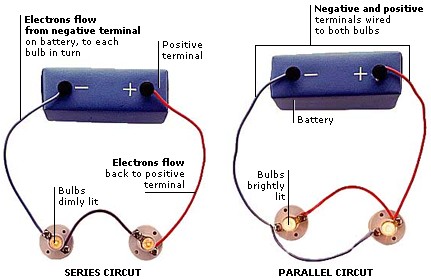
Current only flows when a circuit is complete—when there are no gaps in it. In a complete circuit, the electrons flow from the negative terminal (connection) on the power source, through the connecting wires and components, such as bulbs, and back to the positive terminal.
When a wire is connected to battery terminals, electrons flow from negative to positive. Unlike (opposite) charges attract, like (same) charges repel. Electrons have a negative charge—they are repelled from the negative and attracted to the positive.
A battery is a compact, easily transportable source of electricity. When a battery is connected in a circuit, it provides the energy that drives the electrons along in a current. Batteries contain chemical substances that react together to separate positive and negative charges.
A battery is made of one or more sections or cells. Inside each cell, two chemically active materials called electrodes are separated by a liquid or paste called the electrolyte. Small batteries may have just one cell. Large, powerful batteries may have six cells.
Inside a cell the electrolyte reacts with the electrodes, causing electrons to move through the electrolyte from one electrode to the other. One electrode gains a negative charge and the other a positive charge. The two electrodes are the positive and negative terminals.
The different objects that make up a circuit are called components. A circuit must have a power source, such as a battery, and the current flows through a conductor, such as a wire. Bulbs, buzzers, and motors are components that change electricity into light, sound, and movement.
The battery and other components of an artificial heart pacemaker send electric pulses through wires to a patient’s heart to keep it beating steadily. A pacemaker is put in when the heart does not beat steadily by itself.
A material that carries a current well is called a conductor. Metals are good conductors because metal atoms readily release electrons to carry the current. Silver and copper are the best conductors, and most electric wires are made from copper. To prevent electric shocks, wires are covered with an insulator.
Some materials do not carry current well. They are said to resist (oppose) the flow of current. Materials that do this are called insulators. Plastics, glass, rubber, and ceramics are all good insulators. Insulators are used to cover wires and components to prevent electric shocks, and to stop currents from flowing.
Switches are like gates that control the flow of electricity in a circuit. When a switch is open, it creates a gap in the circuit and current will not flow. When it is closed, it completes the circuit, and current flows through it. Switches are used in parallel circuits to turn different parts of the circuit on and off.