DK Science: Flowering Plants
Known as angiosperms (which means “seed cases”), flowering plants produce seeds inside the swollen base of the FLOWER, the ovary. Flowering plants make up over 80 per cent of all plant species. They are found in most parts of the world and range in size from tiny aquatic duckweed to gigantic eucalyptus trees. Flowering plants are divided into two groups, monocotyledons and dicotyledons.

Flowering plants that have one seed leaf are monocotyledons. Their adult leaves have rows of parallel veins. Their petals and other flower parts are usually in multiples of three.
The largest group of flowering plants, dicotyledons have two seed leaves. Veins branch out along the adult leaves. Their petals and other flower parts usually occur in fours or fives.
Containing a plant’s reproductive organs, flowers are the showy parts of flowering plants. Many depend on animal pollinators, which they attract with their colour, markings, or scent. Some plants, such as lilies, grow single flowers. Other plants produce large clusters of flowers. Daisies and sunflowers have many tiny flowers, or florets, that form a single flowerhead.
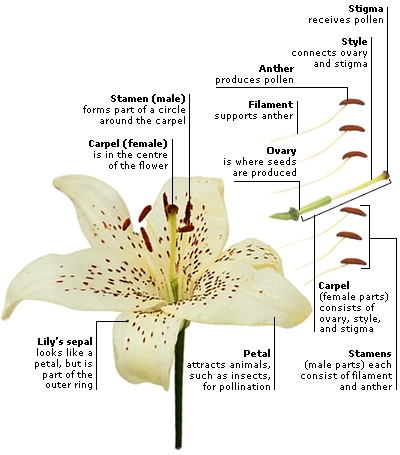
The simplest flowers have their parts arranged in a circle. The outer ring is made up of sepals. These protect the flower when it is in bud. Inside the sepals are the petals. Sometimes, as in the lily, the sepals and petals may look the same. In the centre of the flower are the female parts, which make up the carpel. Around the carpel are the male parts, called stamens.
